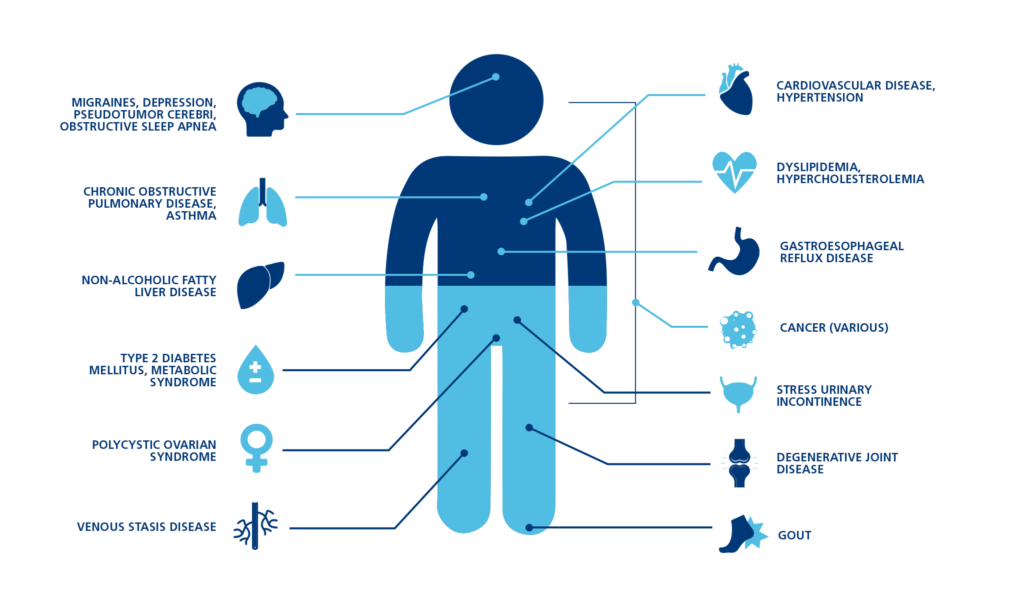
What is Comorbidity?
Comorbidity is the simultaneous presence of two or more diseases or medical conditions in a patient. They may exist together for many reasons, including shared causes and risk factors. Obesity comorbidities increase the health risk in obese patients.
Comorbidities can increase the risk of complications or even cause a development of a new health issue.