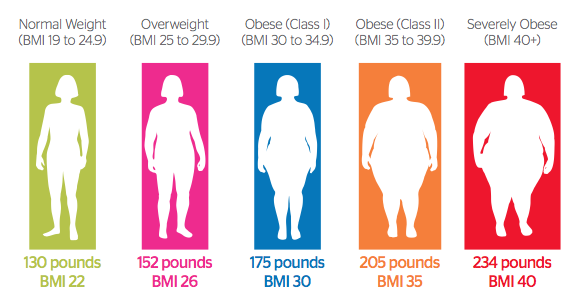
What is Obesity?
Obesity and overweight are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health. It occurs when over time you eat more calories than you can use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out is different for each person. Factors that might affect person’s weight include genetic makeup, overeating, eating high-fat foods, and not being physically active.
It is no longer considered a cosmetic issue that is caused by overeating and a lack of self-control. The World Health Organization (W.H.O.), along with National and International medical and scientific societies, now recognize obesity as a chronic progressive disease resulting from multiple environmental and genetic factors.